Understanding the Critical Role of Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industrial Processes
Understanding the Critical Role of Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industrial Processes Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Heat Exchanger Evaporators 2. The Functionality of Heat Exchanger Evaporators 3. Types of Heat Exchanger Evaporators 4. Benefits of Using Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industries 5. Design Considerations for Effective Heat Exchanger Evaporators 6. Maintenance Practices for Opt
Published:
2025-11-26
source:
author:
Understanding the Critical Role of Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industrial Processes
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Heat Exchanger Evaporators
2. The Functionality of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
3. Types of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
4. Benefits of Using Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industries
5. Design Considerations for Effective Heat Exchanger Evaporators
6. Maintenance Practices for Optimal Performance
7. Industrial Applications of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
8. Future Trends in Heat Exchanger Technology
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Heat Exchanger Evaporators
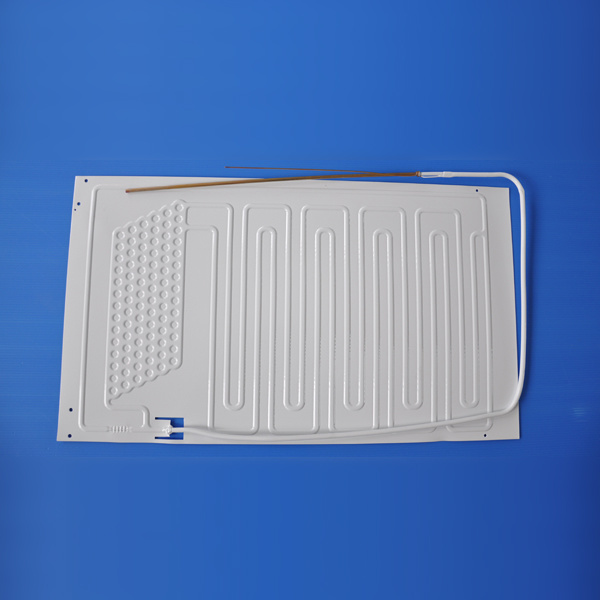
In the realm of industrial processes, **heat exchanger evaporators** play a vital role in enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. These systems are responsible for transferring heat from one medium to another, often facilitating the phase change of liquids into vapors. As industries strive for sustainability and energy efficiency, understanding the importance of these devices becomes essential.
2. The Functionality of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
Heat exchanger evaporators operate by utilizing **thermal energy** to convert liquids into vapor. The process involves two key components: the **heat source** and the **heat sink**. When a liquid is heated, it absorbs energy and gradually transforms into vapor. This vapor can be used for various applications, including heating, cooling, and power generation. The efficiency of this process directly impacts the overall productivity of industrial operations.
2.1 Phase Change Mechanism
The phase change mechanism in heat exchanger evaporators is fundamental to their operation. As the liquid enters the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment. This heat transfer causes the liquid to reach its boiling point, leading to the formation of vapor. The vapor, now at a high energy state, can be utilized in different processes, such as distillation, refrigeration, and chemical reactions.
2.2 Heat Transfer Principles
Effective heat transfer is critical for the optimal performance of evaporators. The **conductive, convective, and radiative** heat transfer mechanisms work in tandem to maximize efficiency. Engineers design evaporators with specific materials and configurations to ensure that heat transfer occurs at an optimal rate, minimizing energy loss and maximizing output.
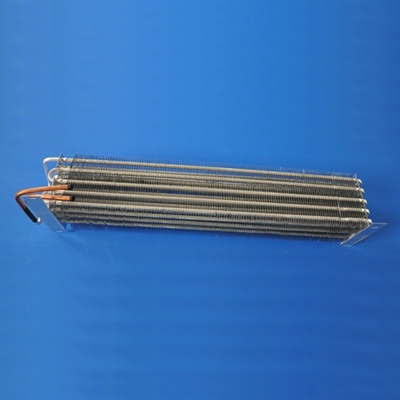
3. Types of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
There are several types of heat exchanger evaporators, each tailored for specific applications and industries. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right system for particular processes.
3.1 Falling Film Evaporators
Falling film evaporators involve a thin film of liquid flowing down the heating surface, allowing for efficient heat transfer and rapid evaporation. This design is particularly useful in concentrating solutions and is widely used in the food and beverage industry.
3.2 Forced Circulation Evaporators
In forced circulation evaporators, a pump circulates the liquid, ensuring a consistent flow rate and promoting effective heat transfer. These evaporators are commonly used in chemical processing and wastewater treatment applications.
3.3 Vacuum Evaporators
Vacuum evaporators operate under reduced pressure, lowering the boiling point of the liquid, which enhances evaporation efficiency. They are ideal for applications involving heat-sensitive materials, such as pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals.
3.4 Plate Evaporators
Plate evaporators consist of multiple plates arranged to create narrow flow channels. This design promotes high heat transfer efficiency and is often employed in industries requiring compact and efficient heat exchangers.
4. Benefits of Using Heat Exchanger Evaporators in Industries
The integration of heat exchanger evaporators into industrial processes offers numerous benefits that contribute to operational efficiency and sustainability.
4.1 Energy Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of heat exchanger evaporators is their ability to utilize waste heat, improving energy efficiency. By recovering energy that would otherwise be lost, industries can significantly reduce their energy consumption and associated costs.
4.2 Cost Savings
Implementing heat exchanger evaporators leads to substantial cost savings over time. With reduced energy consumption and minimized waste, companies can improve their profit margins while maintaining high production levels.
4.3 Enhanced Process Control
Heat exchanger evaporators provide precise control over temperature and pressure, allowing for better process management. This level of control is essential for maintaining product quality and consistency in industrial applications.
4.4 Environmental Sustainability
The use of heat exchanger evaporators supports environmental sustainability initiatives by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing waste. By optimizing energy use, industries can contribute to a greener future.
5. Design Considerations for Effective Heat Exchanger Evaporators
Designing an effective heat exchanger evaporator requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
5.1 Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for construction is critical for the durability and efficiency of evaporators. Materials must withstand high temperatures, corrosive environments, and pressure fluctuations.
5.2 Flow Arrangement
The arrangement of liquid and vapor flow significantly impacts heat transfer efficiency. Engineers must carefully evaluate whether to use counterflow, parallel flow, or crossflow arrangements based on the specific application.
5.3 Heat Transfer Surface Area
Maximizing the heat transfer surface area is essential for improving the efficiency of evaporators. Utilizing advanced designs, such as corrugated plates or enhanced tube geometries, can increase the effective surface area.
6. Maintenance Practices for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of heat exchanger evaporators. Implementing best practices can prevent costly downtime and enhance performance.
6.1 Routine Inspections
Conducting routine inspections allows for the early detection of issues such as leaks, corrosion, or fouling. Regular checks help maintain optimal performance and identify necessary repairs before they escalate.
6.2 Cleaning Procedures
Maintaining clean heat transfer surfaces is vital for efficiency. Implementing cleaning protocols, such as chemical cleaning or mechanical brushing, can prevent fouling and ensure continuous operation.
6.3 Monitoring Performance
Utilizing performance monitoring systems can help track key metrics such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. This data enables timely adjustments to maintain efficiency and prevent failures.
7. Industrial Applications of Heat Exchanger Evaporators
Heat exchanger evaporators find applications across various industries, showcasing their versatility and effectiveness in enhancing industrial processes.
7.1 Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage sector, heat exchanger evaporators are used for concentrating juices, producing dairy products, and processing sauces. Their ability to preserve flavor and nutrients while reducing energy consumption makes them invaluable.
7.2 Chemical Processing
Chemical manufacturers rely on heat exchanger evaporators for the synthesis of various compounds. These systems enable efficient phase changes and heat recovery, contributing to sustainable production practices.
7.3 Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, heat exchanger evaporators play a crucial role in producing active ingredients and concentrating solutions. Their precise control over temperature and pressure is essential for maintaining product integrity.
7.4 Wastewater Treatment
Heat exchanger evaporators are increasingly utilized in wastewater treatment processes. They help recover valuable resources while minimizing environmental impact, aligning with sustainability goals.
8. Future Trends in Heat Exchanger Technology
As industries evolve, so do the technologies surrounding heat exchanger evaporators. Emerging trends reflect the ongoing pursuit of efficiency, sustainability, and innovation.
8.1 Advanced Materials
The use of advanced materials, such as composites and coatings, is gaining traction in heat exchanger design. These materials improve durability and resistance to corrosion, enhancing overall performance.
8.2 Automation and IoT Integration
The integration of automation and the Internet of Things (IoT) into heat exchanger systems allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis. This technology enables predictive maintenance and optimal operational control.
8.3 Energy Recovery Systems
Innovative energy recovery systems are being developed to maximize efficiency. These systems aim to capture and utilize waste heat from evaporators, further enhancing energy conservation.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary function of heat exchanger evaporators?
Heat exchanger evaporators primarily convert liquids into vapor through the transfer of thermal energy, playing a vital role in various industrial processes.
How do heat exchanger evaporators improve energy efficiency?
These systems enhance energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat, reducing overall energy consumption and lowering operational costs.
What are the different types of heat exchanger evaporators?
Common types include falling film evaporators, forced circulation evaporators, vacuum evaporators, and plate evaporators, each suited for specific applications.
Why is maintenance important for heat exchanger evaporators?
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance, prevents costly downtimes, and prolongs the lifespan of evaporators by addressing issues like fouling and leaks.
What industries benefit from heat exchanger evaporators?
Industries such as food and beverage, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment greatly benefit from the use of heat exchanger evaporators.
10. Conclusion
In summary, heat exchanger evaporators are indispensable components in industrial processes, offering significant benefits in terms of energy efficiency, cost savings, and sustainability. As we advance into an era of heightened environmental awareness, the role of these systems will only become more critical. By understanding their functionality, types, and applications, industries can harness the full potential of heat exchanger evaporators, driving innovation and efficiency in their operations.
Hot News
Mobile website

language
English
العربية
বাংলাদেশ
Български
Hrvatski
Česky
Dansk
Nederland
 Esperanto
Esperanto
Slovenski
Filipino
Suomi
Français
Maori
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
Georgian
 Euskara
Euskara
Deutsch
Ελλάδα
ישראל
इंडिया
Magyarország
Ísland
Indonesia
Irlanda
Italia
日本語
Sovensko
Հայաստան
한국
Kyrgyz
ປະເທດລາວ
 Zulu
Zulu
Latvian
Lithuanian
Luxembourgish
 Latinus
Latinus
Macedonian
Малайская
Maltese
Монгол улс
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
ဗမာ
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
नेपाल
Norge
ایران
Polska
Portugal
România
Российская
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Bosanski
Slovenian
Беларус
España
Sverige
Точик
ประเทศไทย
Türk
Azərbaycan
Uzbek
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Việt Nam
Tel: 0086-13775291367
E-mail: michael@xinxincool.com
ADD:No. 32 Tianshan Road, Xinqiao Town, Xinbei District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
Copyright © 2024 Changzhou Xinxin Refrigeration Equipment Co., Ltd.