Choosing the Right Refrigeration Evaporator for Your Industrial Needs
Table of Contents: 1. Introduction: Understanding the Significance of a Refrigeration Evaporator 2. Types of Refrigeration Evaporators 2.1 Forced Air Evaporators 2.2 Liquid Overfeed Evaporators 2.3 Gravity Coil Evaporators 2.4 Plate Evaporators 2.5 Shell and Tube Evaporators 2.6 Finned Evaporators 2.7 Coils-in-Series Evaporators 2.8 Flooded Shell Evaporators 3. Factors to C
Published:
2024-01-18
source:
author:
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction: Understanding the Significance of a Refrigeration Evaporator
2. Types of Refrigeration Evaporators
2.1 Forced Air Evaporators
2.2 Liquid Overfeed Evaporators
2.3 Gravity Coil Evaporators
2.4 Plate Evaporators
2.5 Shell and Tube Evaporators
2.6 Finned Evaporators
2.7 Coils-in-Series Evaporators
2.8 Flooded Shell Evaporators
3. Factors to Consider when Choosing a Refrigeration Evaporator
3.1 Cooling Capacity
3.2 Space and Installation Constraints
3.3 Energy Efficiency
3.4 Maintenance and Cleanliness
3.5 Compatibility with Refrigerants
3.6 Customization Options
3.7 Cost-effectiveness
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
4.1 What is the purpose of a refrigeration evaporator?
4.2 How does a forced air evaporator work?
4.3 Which type of evaporator is best for small spaces?
4.4 Can a refrigeration evaporator be used with different refrigerants?
4.5 What maintenance is required for a refrigeration evaporator?
5. Conclusion
1. Introduction: Understanding the Significance of a Refrigeration Evaporator
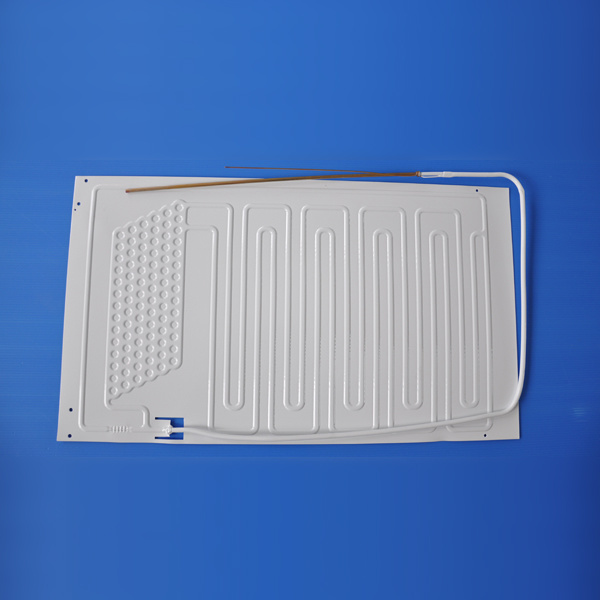
Refrigeration evaporators play a crucial role in industrial cooling systems by absorbing heat from the surroundings and facilitating the cooling process. Selecting the right evaporator is essential for maximizing cooling efficiency and maintaining product integrity.
2. Types of Refrigeration Evaporators
2.1 Forced Air Evaporators
Forced air evaporators use fans to circulate air over the evaporator coil, enhancing heat transfer. They are commonly used in commercial refrigeration units due to their uniform cooling capabilities.
2.2 Liquid Overfeed Evaporators
Liquid overfeed evaporators utilize a continuous flow of liquid refrigerant over the evaporator coil, improving cooling efficiency. They are suitable for large-scale industrial applications that require precise temperature control.
2.3 Gravity Coil Evaporators
Gravity coil evaporators rely on gravity to distribute liquid refrigerant evenly across the evaporator coil. They are commonly used in walk-in coolers and freezers, providing efficient cooling in medium-sized spaces.
2.4 Plate Evaporators
Plate evaporators consist of a series of plates with refrigerant flowing between them. These evaporators offer high heat transfer efficiency and are ideal for applications with limited space.
2.5 Shell and Tube Evaporators
Shell and tube evaporators employ a series of tubes within a shell, facilitating heat exchange between the refrigerant and the surrounding medium. They are widely used in industrial cooling systems.
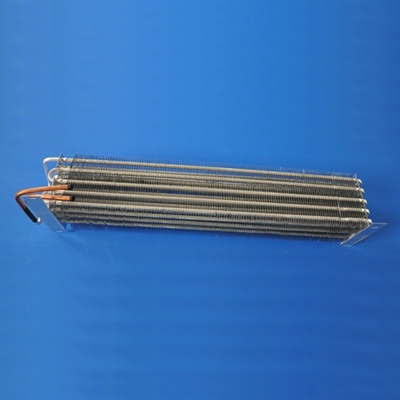
2.6 Finned Evaporators
Finned evaporators feature fins on the evaporator coil surface to increase the heat transfer area, improving cooling efficiency. They are commonly used in air conditioning systems and refrigerated display cases.
2.7 Coils-in-Series Evaporators
Coils-in-series evaporators consist of multiple evaporator coils connected in series. This configuration enables precise cooling control and is often utilized in critical industrial applications.
2.8 Flooded Shell Evaporators
Flooded shell evaporators submerge the evaporator tubes in liquid refrigerant, ensuring efficient heat transfer. They are suitable for large-scale industrial refrigeration systems.
3. Factors to Consider when Choosing a Refrigeration Evaporator
3.1 Cooling Capacity
Assess your cooling requirements and choose an evaporator that can efficiently handle the desired cooling capacity while maintaining optimal temperature levels.
3.2 Space and Installation Constraints
Consider the available space and installation requirements. Select an evaporator that fits within the allocated space and can be installed seamlessly with the existing refrigeration system.
3.3 Energy Efficiency
Opt for an energy-efficient evaporator to reduce operating costs and minimize environmental impact. Look for energy-saving features such as variable speed fans or advanced heat transfer technologies.
3.4 Maintenance and Cleanliness
Choose an evaporator that is easy to clean and maintain. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment.
3.5 Compatibility with Refrigerants
Ensure the chosen evaporator is compatible with the specific refrigerant used in your cooling system. Different evaporator designs may require specific refrigerant types for optimal functioning.
3.6 Customization Options
Consider the flexibility of customization options offered by the evaporator manufacturer. Customizable features can better cater to your unique cooling requirements.
3.7 Cost-effectiveness
Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the evaporator, including initial investment, operating expenses, maintenance, and potential energy savings. Choose a cost-effective option that aligns with your budget.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
4.1 What is the purpose of a refrigeration evaporator?
A refrigeration evaporator absorbs heat from the surroundings, facilitating the cooling process in industrial refrigeration systems.
4.2 How does a forced air evaporator work?
A forced air evaporator uses fans to circulate air over the evaporator coil, enhancing heat transfer and providing uniform cooling.
4.3 Which type of evaporator is best for small spaces?
Gravity coil evaporators are often the preferred choice for small spaces, such as walk-in coolers or freezers, due to their efficient cooling capabilities.
4.4 Can a refrigeration evaporator be used with different refrigerants?
Yes, the compatibility of a refrigeration evaporator with different refrigerants depends on its design and specifications. Consult with the manufacturer to ensure compatibility.
4.5 What maintenance is required for a refrigeration evaporator?
Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to maintain optimal performance. This includes removing dust, debris, and ice buildup from the evaporator coil.
5. Conclusion
Selecting the right refrigeration evaporator is crucial for optimizing your industrial cooling system. Consider factors such as cooling capacity, space constraints, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements to make an informed decision. By choosing the appropriate evaporator, you can ensure efficient cooling, reduce operating costs, and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
1. Introduction: Understanding the Significance of a Refrigeration Evaporator
2. Types of Refrigeration Evaporators
2.1 Forced Air Evaporators
2.2 Liquid Overfeed Evaporators
2.3 Gravity Coil Evaporators
2.4 Plate Evaporators
2.5 Shell and Tube Evaporators
2.6 Finned Evaporators
2.7 Coils-in-Series Evaporators
2.8 Flooded Shell Evaporators
3. Factors to Consider when Choosing a Refrigeration Evaporator
3.1 Cooling Capacity
3.2 Space and Installation Constraints
3.3 Energy Efficiency
3.4 Maintenance and Cleanliness
3.5 Compatibility with Refrigerants
3.6 Customization Options
3.7 Cost-effectiveness
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
4.1 What is the purpose of a refrigeration evaporator?
4.2 How does a forced air evaporator work?
4.3 Which type of evaporator is best for small spaces?
4.4 Can a refrigeration evaporator be used with different refrigerants?
4.5 What maintenance is required for a refrigeration evaporator?
5. Conclusion
1. Introduction: Understanding the Significance of a Refrigeration Evaporator
Refrigeration evaporators play a crucial role in industrial cooling systems by absorbing heat from the surroundings and facilitating the cooling process. Selecting the right evaporator is essential for maximizing cooling efficiency and maintaining product integrity.
2. Types of Refrigeration Evaporators
2.1 Forced Air Evaporators
Forced air evaporators use fans to circulate air over the evaporator coil, enhancing heat transfer. They are commonly used in commercial refrigeration units due to their uniform cooling capabilities.
2.2 Liquid Overfeed Evaporators
Liquid overfeed evaporators utilize a continuous flow of liquid refrigerant over the evaporator coil, improving cooling efficiency. They are suitable for large-scale industrial applications that require precise temperature control.
2.3 Gravity Coil Evaporators
Gravity coil evaporators rely on gravity to distribute liquid refrigerant evenly across the evaporator coil. They are commonly used in walk-in coolers and freezers, providing efficient cooling in medium-sized spaces.
2.4 Plate Evaporators
Plate evaporators consist of a series of plates with refrigerant flowing between them. These evaporators offer high heat transfer efficiency and are ideal for applications with limited space.
2.5 Shell and Tube Evaporators
Shell and tube evaporators employ a series of tubes within a shell, facilitating heat exchange between the refrigerant and the surrounding medium. They are widely used in industrial cooling systems.
2.6 Finned Evaporators
Finned evaporators feature fins on the evaporator coil surface to increase the heat transfer area, improving cooling efficiency. They are commonly used in air conditioning systems and refrigerated display cases.
2.7 Coils-in-Series Evaporators
Coils-in-series evaporators consist of multiple evaporator coils connected in series. This configuration enables precise cooling control and is often utilized in critical industrial applications.
2.8 Flooded Shell Evaporators
Flooded shell evaporators submerge the evaporator tubes in liquid refrigerant, ensuring efficient heat transfer. They are suitable for large-scale industrial refrigeration systems.
3. Factors to Consider when Choosing a Refrigeration Evaporator
3.1 Cooling Capacity
Assess your cooling requirements and choose an evaporator that can efficiently handle the desired cooling capacity while maintaining optimal temperature levels.
3.2 Space and Installation Constraints
Consider the available space and installation requirements. Select an evaporator that fits within the allocated space and can be installed seamlessly with the existing refrigeration system.
3.3 Energy Efficiency
Opt for an energy-efficient evaporator to reduce operating costs and minimize environmental impact. Look for energy-saving features such as variable speed fans or advanced heat transfer technologies.
3.4 Maintenance and Cleanliness
Choose an evaporator that is easy to clean and maintain. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment.
3.5 Compatibility with Refrigerants
Ensure the chosen evaporator is compatible with the specific refrigerant used in your cooling system. Different evaporator designs may require specific refrigerant types for optimal functioning.
3.6 Customization Options
Consider the flexibility of customization options offered by the evaporator manufacturer. Customizable features can better cater to your unique cooling requirements.
3.7 Cost-effectiveness
Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the evaporator, including initial investment, operating expenses, maintenance, and potential energy savings. Choose a cost-effective option that aligns with your budget.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
4.1 What is the purpose of a refrigeration evaporator?
A refrigeration evaporator absorbs heat from the surroundings, facilitating the cooling process in industrial refrigeration systems.
4.2 How does a forced air evaporator work?
A forced air evaporator uses fans to circulate air over the evaporator coil, enhancing heat transfer and providing uniform cooling.
4.3 Which type of evaporator is best for small spaces?
Gravity coil evaporators are often the preferred choice for small spaces, such as walk-in coolers or freezers, due to their efficient cooling capabilities.
4.4 Can a refrigeration evaporator be used with different refrigerants?
Yes, the compatibility of a refrigeration evaporator with different refrigerants depends on its design and specifications. Consult with the manufacturer to ensure compatibility.
4.5 What maintenance is required for a refrigeration evaporator?
Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary to maintain optimal performance. This includes removing dust, debris, and ice buildup from the evaporator coil.
5. Conclusion
Selecting the right refrigeration evaporator is crucial for optimizing your industrial cooling system. Consider factors such as cooling capacity, space constraints, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements to make an informed decision. By choosing the appropriate evaporator, you can ensure efficient cooling, reduce operating costs, and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
Hot News
Mobile website

language
English
العربية
বাংলাদেশ
Български
Hrvatski
Česky
Dansk
Nederland
 Esperanto
Esperanto
Slovenski
Filipino
Suomi
Français
Maori
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
Georgian
 Euskara
Euskara
Deutsch
Ελλάδα
ישראל
इंडिया
Magyarország
Ísland
Indonesia
Irlanda
Italia
日本語
Sovensko
Հայաստան
한국
Kyrgyz
ປະເທດລາວ
 Zulu
Zulu
Latvian
Lithuanian
Luxembourgish
 Latinus
Latinus
Macedonian
Малайская
Maltese
Монгол улс
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
ဗမာ
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
नेपाल
Norge
ایران
Polska
Portugal
România
Российская
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Bosanski
Slovenian
Беларус
España
Sverige
Точик
ประเทศไทย
Türk
Azərbaycan
Uzbek
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Việt Nam
Tel: 0086-13775291367
E-mail: michael@xinxincool.com
ADD:No. 32 Tianshan Road, Xinqiao Town, Xinbei District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
Copyright © 2024 Changzhou Xinxin Refrigeration Equipment Co., Ltd.